|
Important Note for Users: In order to
avoid infection or reinfection from Win32.Poza, it is vital
that your machine has been patched to address the Dcom RPC
vulnerabilty that the worm exploits. Systems running Windows
XP, 2000 and NT 4.0 are vulnerable to this exploit. Please
visit Microsoft to download the relevant patch at: Manichiura clasica.
You will need to reboot your machine after installing the
patch in order for this update to take effect.
Cleaning Utility Available: To
download ClnPoza.zip - a utility that cleans a
local machine affected by Win32.Poza, please
click here.
This utility may be especially useful for those who either
do not use CA Antivirus solutions, or who may be using
products based on older technology that does not support
system cleaning. Please view the Removal Instructions for your
CA Antivirus Solution (below) to ascertain whether you require
the cleaning utility.
Warning: Before running ClnPoza.com,
please ensure that you carefully review the ReadMe.txt
instruction file that accompanies this utility.
--------------------
Win32.Poza is a worm using the exploit described in
MS03-026 to gain access to unpatched Windows
installations. More information about the exploit can be
found in our Vulnerabilities
Library or at the Microsoft site here: Manichiura clasica
Method of Installation
It creates a mutex "BILLY" to avoid running
multiple instances of itself, and creates a registry value to
activate on Windows restart:
SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run\windows
auto update = "msblast.exe"
The worm runs a TFTP service listening on port 69 waiting
for exploited machine to connect.
Method of Distribution
It starts by scanning the entire subnet for open 135
ports, then moves on to scan randomly selected class B subnets
(255.255.0.0) to start scanning. If an open 135
port is found, it uses the exploit mentioned above to gain
entry and create a remote shell on the exploited
machine. It then assumes the exploit succeeded and
attempts to connect to port 4444 of the remote
machine. If successfully connected, it instructs the
remote machine to download MSBLAST.EXE (size: 6,176
bytes, UPX packed) from its TFTP (Trivial File
Transfer Protocol) service using TFTP.EXE. It
then sends an instruction to start MSBLAST.EXE on the
remote machine.
Note: TFTP.EXE is a utility
included in default installations of Windows
2000 and later versions.
The worm is capable of keeping live connections to
20 exploited machines simultaneously.
The worm attempts to infect both Windows 2000 and Windows
XP systems. One of the offsets used by the worm must be
different for each of these operating systems, in order for
the exploit it uses to work. Since the worm does not know what
operating system the target machine is running, it guesses.
There is an 80% chance it will attempt to exploit Windows XP,
and a 20% chance it will attempt to exploit Windows 2000.
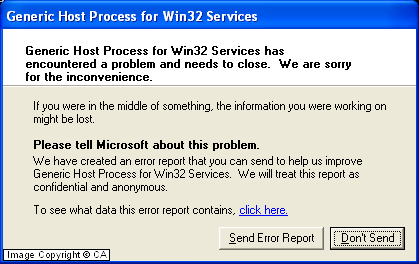
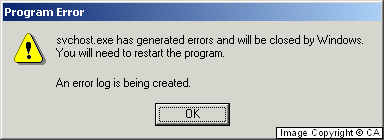
If the worm guesses incorrectly and the remote machine is
vulnerable, the process svchost.exe on the target machine will
crash. The system may become unstable, but the infection
will fail. When svchost.exe crashes, a message like this
may appear on Windows XP:
And on Windows 2000:
Windows XP systems may automatically reboot at this
point.
If the worm guesses correctly and the remote machine is
vulnerable, the worm will infect it. If the worm disconnects
from the remote machine, the scvhost.exe process it was
connected to will exit. On Windows XP, this may cause the
machine to reboot, after the following message box is
displayed:
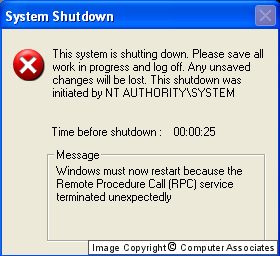
In our laboratory testing, there was no obvious effect
on Windows 2000 machines, except that they no longer listened
on port 135.
Note: When svchost.exe crashes, Windows
may create memory dumps of the process. These files are
usually called user.dmp, svchost.exe.hdmp, or
svchost.exe.mdmp. Because these files contain the exploit code
that caused the crash, they may be detected as DcomRpc.exploit
or MS03-026 Exploit.Trojan. These files are harmless, and can
safely be deleted. However, the existence of these files
indicates that the system was vulnerable to the exploit at the
time they were created, and may still need to be patched.
Payload
If the day of the month is 16 or later, or the
month is September or later, the worm creates a working
thread to send multiple TCP connection requests (SYNs) to
windowsupdate.com almost continuously. This effectively
launches a Distributed
Denial of Service attack against windowsupdate.com.
In order to attempt to create a Denial of
Service state on windowsupdate.com (a condition that
occurs when a system's networking resources are exhausted to
the point that it is not longer able to respond to new or
legitimate requests or connections), it appears that Poza
attempts what is known as a SYN
Flood Attack.
In order to carry out this form of attack, Poza sends one
SYN TCP packet every 20 milliseconds with a spoofed
random IP source address via a local port (between 1000
and 1999) to port 80 (http) on windowsupdate.com, with a
random sequence number and a static window size of
16384. Please see our Glossary
for further details on SYN Flood Attacks.
Additional Information
The worm body contains these strings:
I just want to say LOVE YOU SAN!!
billy gates why do
you make this possible ? Stop making money and fix your
software!!
Analysis by Sha-Li Hsieh, Oleg Petrovsky and Hamish
O'Dea |